EtherIP South Plugin¶
The foglamp-south-etherip plugin is a south plugin that supports PLC Tags read operation for Allen Bradley/Rockwell PLCs. This is based on libplctag and API level details can be read at wiki
Configuration Parameters¶
An EtherIP south service is added in the same way as any other south service in FogLAMP,
Select the South menu item
Click on the + icon in the top right
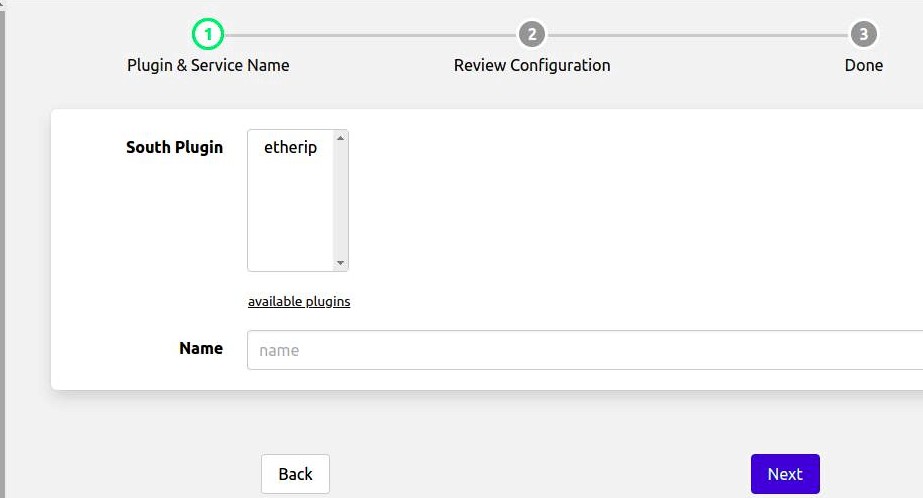
You will be presented with the following page
|
Select etherip from the plugin list
Enter a name for your etherip service
Click Next
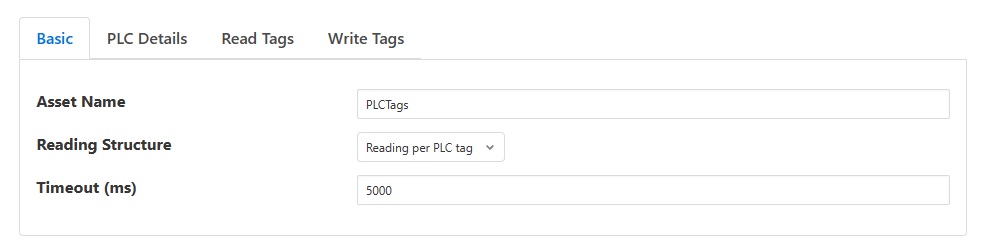
You will be presented with the following configuration page
|
Asset Name: This is the name of the asset that will be used for the data read by this service. This will be used either as a prefix for the asset name, if a unique asset is created for each PLC tag or as the actual asset name if a single reading is created. If the asset names are given in the PLC map then this option will be ignored.
Reading Structure: This option controls the way in which the readings will be structured within FogLAMP. Three options are available; “Reading per asset”, “Reading per PLC tag” or “Single Reading”.
- Reading per asset
One reading will be created for each distinct asset defined in the PLC map.
- Reading per PLC tag
A separate reading will be created for each PLC tag read from the PLC.
- Single Reading
All PLC tags will be read and added to a single asset.
Timeout (ms): The request timeout when communicating with a PLC device. Default value is 5000 (milliseconds). Set this timeout value suitably based on number of tags to read/write and network conditions/RTT/latency, etc.
Error Handling: This option controls the behaviour when an error is encountered reading data from the PLC.
- Only return data if all data is available
Data is returned if all the tags have been read without error from PLC device.
- Return subset of data in case of error
Data is returned only for the tags that are read successfully, error is logged for the tags which have error during reading from PLC device.
|
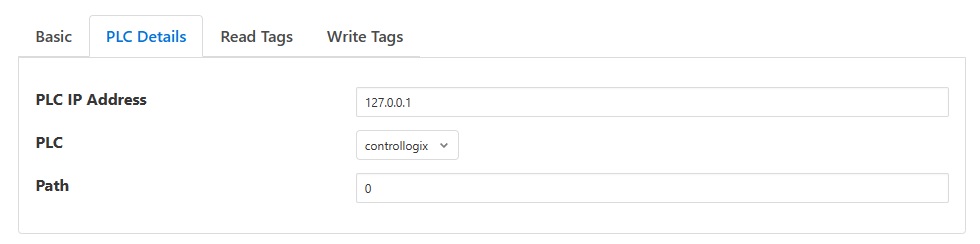
PLC IP Address: This is the IP Address of the PLC Tags server, Default value 127.0.0.1
PLC: This is the type of the PLC from which the user wants to read the tags, Default value controllogix, the following have been supported:
Allen-Bradley ControlLogix & CompactLogix PLCs
Allen-Bradley Micro8x0 PLCs
Rockwell/Allen-Bradley PLCs accessed over a DH+ bridge (i.e. a LGX chassis with a DHRIO module) such as PLC/5, SLC 500 and MicroLogix
Omron NX/NJ series PLCs as for Allen-Bradley Micro8x0
Path: This is the slot/rack(e.g. 0,1) to use to connect to your PLCTags device. This attribute is required for CompactLogix/ControlLogix tags and for tags using a DH+ protocol bridge (i.e. a DHRIO module) to get to a PLC/5, SLC 500, or MicroLogix PLC on a remote DH+ link. The attribute is ignored if it is not a DH+ bridge route, but will generate a warning if debugging is active. Note that Micro8x0 connections must not have a path attribute.
|
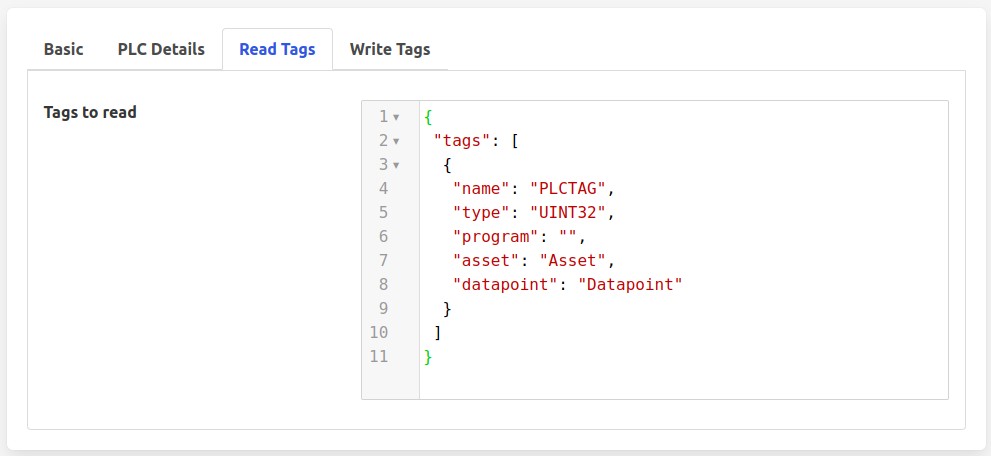
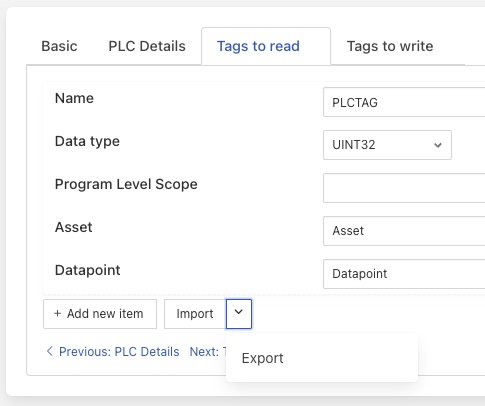
Tags to read: The list of PLCTags the user wishes to read. Each item in the list comprises of 5 elements. For details of these elements and how to interaction with the list see below.
|
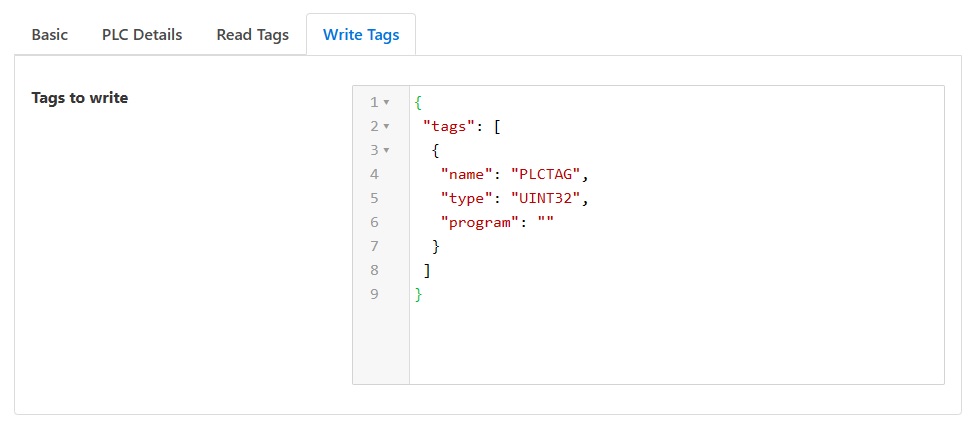
Tags to write: The list of PLCTags the user wishes to enable for control operations to write to the PLC. Each item in the list comprises of 5 elements. For details of these elements and how to interaction with the list see below.
Tag Lists¶
The list of tags to read/write comprises of 5 elements shown in the table below. Each entry in the list represents a single tag in the PLC. Each tag will be stored in FogLAMP or written by set-point control.
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
The name of the PLCTag that we are reading/writing. In case of read, this becomes the name of the datapoint with the asset. |
Data type |
The datatype of the PLCTag that we are reading/writing. |
Program level Scope |
This defines the scope of the PLCTag that we are reading/writing, possible values being Program level scope or Global/Controller level scope. The Program name needs to be specified here if it is a tag with program level scope. For global/controller level tags ‘program’ attribute in map can be omitted or set to JSON null value or empty. |
Asset |
The asset name associated with the PLC when read or used for a write operation. |
Datapoint |
The datapoint name to use within the asset. |
A number of different types are supported by the plugin, these map to the underlying types that are supported by the various PLCs. The table below lists the types that are currently supported within the plugin.
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
BOOL |
A single bit boolean field |
BIT |
A single bit field |
BYTE |
An 8 bit unsigned integer value |
WORD |
A 16 bit unsigned integer value |
DWORD |
A 32 bit unsigned integer value |
INT8 |
An 8 bit signed integer value |
INT16 |
A 16 bit signed integer value |
INT32 |
A 32 bit signed integer value |
INT64 |
A 64 bit signed integer value |
INT |
A 16 bit signed integer value |
USINT |
An 8 bit unsigned integer value |
UINT |
A 16 bit unsigned integer value |
UDINT |
A 32 bit unsigned integer value |
SINT |
An 8 bit signed integer value |
DINT |
A 32 bit signed integer value |
UINT8 |
An 8 bit unsigned integer value |
UINT16 |
A 16 bit unsigned integer value |
UINT32 |
A 32 bit unsigned integer value |
UINT64 |
A 64 bit unsigned integer value |
FLOAT32 |
A 32 bit floating point number |
FLOAT64 |
A 64 bit floating point number |
REAL |
A 32 bit floating point number |
LREAL |
A 64 bit floating point number |
STRING |
An ASCII string value |
SHORT STRING |
An ASCII string value |
Interacting With The List¶
Each item in the list has two controls to the right-hand side of the item
|
The control on the left allows you to delete this list item. The control on the right allows the list item to be collapsed to a smaller form. When collapsed the display changes to that shown below.
|
When collapse a new icon appears, 3 dots. As shown above, hovering over this will cause a summary of the list item to be shown, clicking on it will open up the list item.
There are a number of control at the bottom of the list that can be used to interact with the list as a whole.
Add new item - clicking on this will create a new list item, allowing another tag to be added. Default values will be populated, and the user can modify those values as needed
Import - clicking on this will enable a list to be imported from an external file, more detail is shown below. Clicking on the arrow next to the Import will bring up an Export option which will export the current list to a file.
Two file formats are supported for import and export, a comma separated variable (CSV) format and a JSON format.
The CSV file should contain a header row with the names of the list items, as defined in the plugin configuration and one or more rows of data. The heading columns that are provided are;
Header |
Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of the PLC Tag to read. |
type |
The data type of the PLC Tag. This should be one of the supported types from the table above. |
program |
The program name if the tag has program level scope. |
asset |
The asset name to use in the FogLAMP reading for this tag. |
datapoint |
The datapoint name to use for the PLC tag. |
An example CSV file is shown below;
name,type,program,asset,datapoint
speed,UINT32,,speed,RPM
temperature,REAL,,motor,temperature
Note
A blank is included in the data shown above for the program, which is not required for these tags.
The JSON format is an array of JSON objects, each object has a property for each of the list items, the names of these properties are the same as the header row names listed in the table above. The example below is the JSON equivalent to the CSV example above;
[
{
"name": "speed",
"type": "UINT32",
"program": "",
"asset": "speed",
"datapoint": "RPM"
},
{
"name": "temperature",
"type": "REAL",
"program": "",
"asset": "motor",
"datapoint": "temperature"
}
]
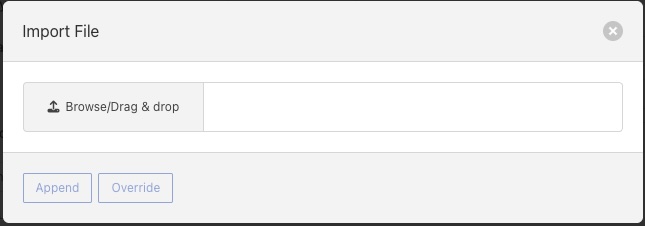
Clicking on the Import option will bring up a popup that allows you to select a file from your local machine or drag and drop a file onto the dialog.
|
You are also presented with the option to Append the file contents to the current list of tags or Override the current list with the contents of the file.
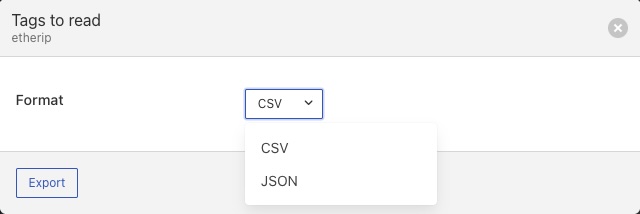
Clicking on Export will present a dialog that request the format to export the data in.
|
Once the format is chosen the data will be written to a file called <service name>-map with an extension of csv or json depending on the format chosen. Where <service name> is the name of the service.
Example Tag Lists¶
In this example, we will assume we have a Micro8x0 PLC, and we want to read one tag with name Tag1, of type UINT32 and having global/controller level scope. Also we want to write to a tag with name Tag2, of type UDINT and having global/controller level scope. We will also assume we want to read the data into an asset called MyAsset and use a datapoint called value.
The Tags to read list attribute for this example would be as follow:
Name |
Tag1 |
|---|---|
Data type |
UINT32 |
Program Level Scope |
|
Asset |
MyAsset |
Datapoint |
value |
Note
It is extremely important that the list be correctly configured with the correct type for each tag that is read. FogLAMP has no way to verify the type that the user requests is the type defined in the PLC, if the type configured for a tag is incorrect then the values read may be meaningless.
A Program Level Scope is not required by this PLC and is therefore left blank.
See Also¶
foglamp-south-ABB - A south plugin to pull data from the ABB cloud
foglamp-south-Beckhoff - A Beckhoff ADS data ingress plugin for FogLAMP, this monitors Beckhoff PLCs and returns the state of internal variables within the PLC
foglamp-south-ModbusC - A FogLAMP south plugin that implements modbus-tcp and modbus-rtu
foglamp-south-S7 - A south plugin that uses the S7 Communications protocol to read data from a Siemens S7 series PLC.
foglamp-south-dnp3 - A south plugin for FogLAMP that implements the DNP3 protocol
foglamp-south-opcua - A FogLAMP south service that pulls data from an OPC-UA server
foglamp-south-s2opcua - An OPC UA south plugin based on the Systerel S2OPC OPC UA Toolkit. This plugin offers similar functionality to the foglamp-south-opcua plugin but also offers data encryption and authentication.