Partition Filter¶
The foglamp-filter-partition filter provides flexible string splitting capabilities for FogLAMP data pipelines. It allows you to split a single string datapoint into multiple new datapoints using configurable delimiters and component mappings.
The filter works by taking a specified source datapoint (which must be of string type), splitting it using a configurable delimiter, and then creating new datapoints based on position mappings defined in the configuration. This is particularly useful for:
Extracting components from hierarchical paths (e.g.,
/organization/factory/line/machine)Normalizing data structures by breaking down complex strings
Creating structured data from delimited text fields
Key Features¶
The partition filter supports several configurable actions for handling various scenarios:
- Source Datapoint Handling:
No action: Keep the original source datapoint unchanged
Remove: Remove the source datapoint after processing
- Missing Portion Actions (when split results have fewer parts than expected):
Use Default: Use configured default values for missing components
Ignore: Skip creating datapoints for missing components
Error Reading: Treat as an error condition
- Error Actions (when processing fails):
Discard Reading: Remove the entire reading from the pipeline
Label Reading: Add an error label datapoint to the reading
Rename Reading: Change the asset name to indicate error condition
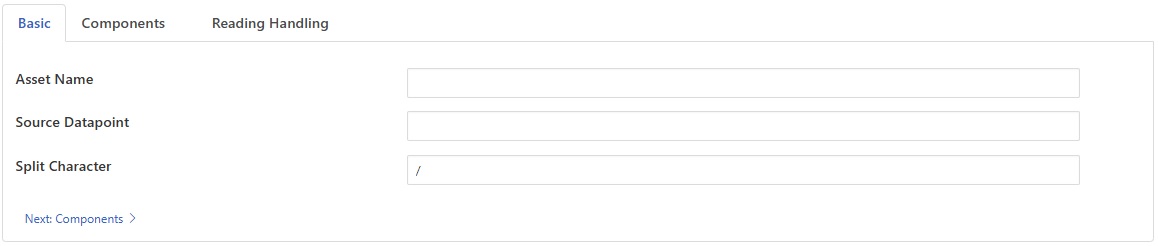
Filter Configuration¶
|
The configuration options supported by the partition filter are:
Asset Name: The name of the asset to process. If left empty, the filter processes all assets.
Source Datapoint: The name of the string datapoint to split. This datapoint must exist and be of string type for processing to occur.
Split Character: The delimiter to use for splitting the string. Defaults to
/but can be any character or string.Enable: Toggle to enable or disable the filter processing.
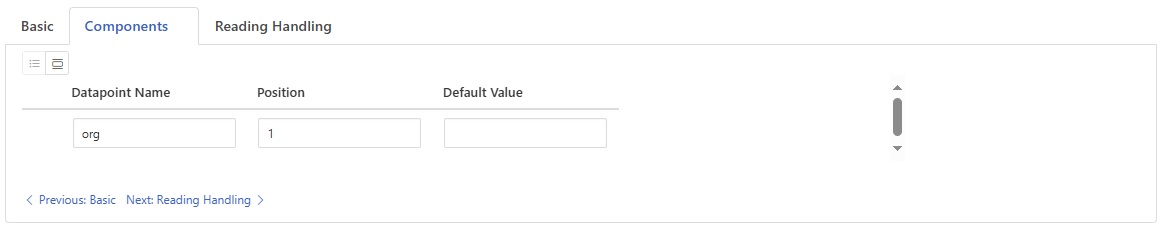
Component Mapping Configuration¶
|
The Components section defines how split parts are mapped to new datapoints:
Datapoint Name: The name of the new datapoint to create from the split component.
Position: The position in the split string (1-based indexing) to use for this datapoint.
Default Value: Optional default value to use if the position is not available in the split result.
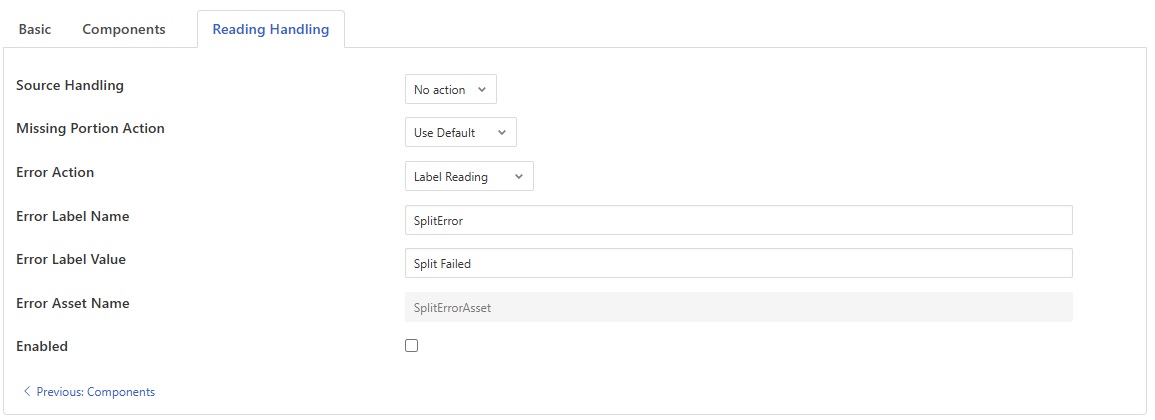
Reading Handling Options¶
|
The filter provides several options for handling the source datapoint and error conditions:
- Source Handling:
No action: Keep the original source datapoint in the reading
Remove: Remove the source datapoint after successful processing
- Missing Portion Action: Defines behavior when the split string has fewer parts than expected:
Use Default: Use the configured default value for missing components
Ignore: Skip creating datapoints for missing positions
Error Reading: Treat insufficient parts as an error condition
- Error Action: Defines behavior when processing fails (wrong datapoint type, missing source, etc.):
Discard Reading: Remove the entire reading from the pipeline
Label Reading: Add error information to the reading
Rename Reading: Change the asset name to indicate error
When using error labeling or renaming, additional configuration options are available:
Error Label Name: The name of the datapoint to add when labeling failed readings (default: “SplitError”).
Error Label Value: The value to assign to the error label datapoint (default: “Split Failed”).
Error Asset Name: The new asset name to use when renaming failed readings (default: “SplitErrorAsset”).
Enabled: Toggle to enable or disable plugin.
Usage Examples¶
Example 1: Hierarchical Path Processing
Input reading with datapoint path = "/acme/factory1/line5/machine12"
- Configuration:
Split Character:
/Components: - org (position 1) → “acme” - factory (position 2) → “factory1” - line (position 3) → “line5” - machine (position 4) → “machine12”
Result: Four new datapoints created with the extracted components.
Example 2: CSV Data Processing
Input reading with datapoint data = "sensor1,25.5,active"
- Configuration:
Split Character:
,Components: - sensor_id (position 1) → “sensor1” - temperature (position 2) → “25.5” - status (position 3) → “active”
Result: Three new datapoints created from the comma-separated values.
Example 3: Error Handling with Defaults
Input reading with datapoint path = "/acme/factory1" (only 2 parts)
- Configuration expecting 4 components with defaults:
Missing Portion Action: “Use Default”
Components with defaults for positions 3 and 4
Result: Two datapoints from available parts, two datapoints with default values.
Example 4: CSV Data Processing with missing values
Input reading with datapoint data = "sensor1,,active"
- Configuration:
Split Character:
,Components: - sensor_id (position 1) → “sensor1” - temperature (position 2) → “” - status (position 3) → “active”
Result: Three new datapoints created from the comma-separated values. The second datapoint for temperature will be empty, as it was not provided in the input string.
See Also¶
foglamp-filter-asset-conformance - A plugin for performing basic sanity checking on the data flowing in the pipeline.
foglamp-filter-asset-validation - A plugin for performing basic sanity checking on the data flowing in the pipeline.
foglamp-filter-batch-label - A filter to attach batch labels to the data. Batch numbers are updated based on conditions seen in the data stream.
foglamp-filter-conditional-labeling - Attach labels to the reading data based on a set of expressions matched against the data stream.
foglamp-filter-consolidation - A Filter plugin that consolidates readings from multiple assets into a single reading
foglamp-filter-ednahint - A hint filter for controlling how data is written using the eDNA north plugin to AVEVA’s eDNA historian
foglamp-filter-enumeration - A filter to map between symbolic names and numeric values in a datapoint.
foglamp-filter-expression - A FogLAMP processing filter plugin that applies a user define formula to the data as it passes through the filter
foglamp-filter-fft - A FogLAMP processing filter plugin that calculates a Fast Fourier Transform across sensor data
foglamp-filter-inventory - A plugin that can inventory the data that flows through a FogLAMP pipeline.
foglamp-filter-md5 - FogLAMP md5 filter computes a MD5 hash of a reading’s JSON representation and stores the hash as a new datapoint within the reading.
foglamp-filter-md5verify - FogLAMP MD5 Verify plugin verifies the integrity of readings by computing a new MD5 hash and comparing it against the stored MD5 datapoint.
foglamp-filter-metadata - A FogLAMP processing filter plugin that adds metadata to the readings in the data stream
foglamp-filter-name-conformance - A FogLAMP filter plugin to enforce unified namespace conformance by validating asset and datapoint names using pattern or lookup rules, with flexible actions for non-conformance.
foglamp-filter-omfhint - A filter plugin that allows data to be added to assets that will provide extra information to the OMF north plugin.
foglamp-filter-python35 - A FogLAMP processing filter that allows Python 3 code to be run on each sensor value.
foglamp-filter-regex - Regular expression filter to match & replace the string datapoint values
foglamp-filter-replace - Filter to replace characters in the names of assets and data points in readings object.
foglamp-filter-rms - A FogLAMP processing filter plugin that calculates RMS value for sensor data
foglamp-filter-scale - A FogLAMP processing filter plugin that applies an offset and scale factor to the data
foglamp-filter-scale-set - A FogLAMP processing filter plugin that applies a set of sale factors to the data
foglamp-filter-sha2 - FogLAMP sha2 filter computes a SHA-2 hash of a reading’s JSON representation and stores the hash as a new datapoint within the reading.
foglamp-filter-sha2verify - FogLAMP SHA2 Verify plugin verifies the integrity of readings by computing a new SHA-2 hash and comparing it against the stored SHA-2 datapoint.
foglamp-filter-sigmacleanse - A data cleansing plugin that removes data that differs from the mean value by more than x sigma
foglamp-filter-statistics - Generic statistics filter for FogLAMP data that supports the generation of mean, mode, median, minimum, maximum, standard deviation and variance.