North HTTP¶
The foglamp-north-http plugin allows data to be sent from the north of one FogLAMP instance into the south of another FogLAMP instance. It allows hierarchies of FogLAMP instances to be built. The FogLAMP to which the data is sent must run the corresponding South service in order for data to flow between the two FogLAMP instances. The plugin supports both HTTP and HTTPS transport protocols and sends a JSON payload of reading data in the internal FogLAMP format.
The plugin may also be used to send data from FogLAMP to another system, the receiving system should implement a REST end point that will accept a POST request containing JSON data. The format of the JSON payload is described below. The required REST endpoint path is defined in the configuration of the plugin.
Filters may be applied to the connection in either the north task that loads this plugin or the receiving south service on the up stream FogLAMP.
A C++ version of this plugin exists also that performs the same function as this plugin, the pair are provided for purposes of comparison and the user may choose whichever they prefer to use.
To create a north task to send to another FogLAMP you should first create the South service that will receive the data. Then create a new north tasks by;
Selecting North from the left hand menu bar.
Click on the + icon in the top left
Choose http_north from the plugin selection list
Name your task
Click on Next
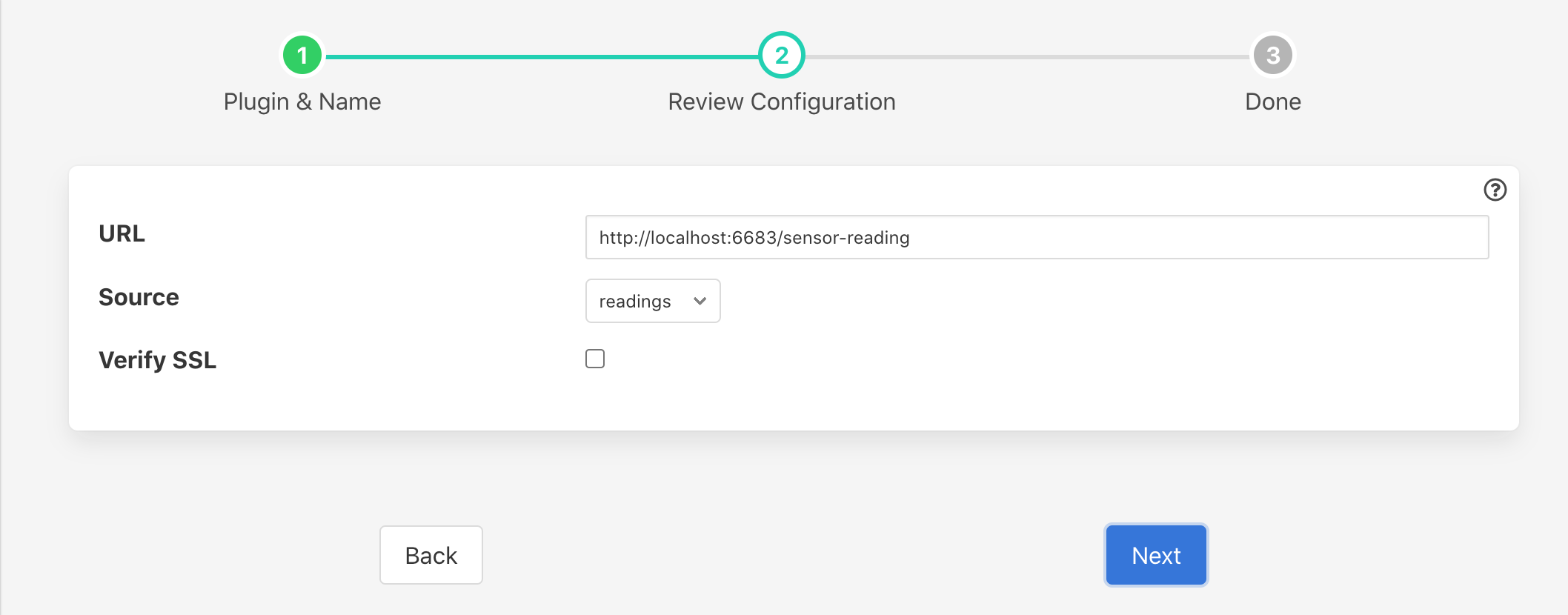
Configure the plugin
URL: The URL of the receiving South service, the address and port should match the service in the up stream FogLAMP. The URL can specify either HTTP or HTTPS protocols.
Source: The data to send, this may be either the reading data or the statistics data
Verify SSL: When HTTPS rather the HTTP is used this toggle allows for the verification of the certificate that is used. If a self signed certificate is used then this should not be enabled.
Click Next
Enable your task and click Done
JSON Payload¶
The payload that is sent by this plugin is a simple JSON presentation of a set of reading values. A JSON array is sent with one or more reading objects contained within it. Each reading object consists of a timestamp, an asset name and a set of data points within that asset. The data points are represented as name value pair JSON properties within the reading property.
The fixed part of every reading contains the following
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
timestamp |
The timestamp as an ASCII string in ISO 8601 extended format. If no time zone information is given it is assumed to indicate the use of UTC. |
asset |
The name of the asset this reading represents. |
readings |
A JSON object that contains the data points for this asset. |
The content of the readings object is a set of JSON properties, each of which represents a data value. The type of these values may be integer, floating point, string, a JSON object or an array of floating point numbers.
A property
"voltage" : 239.4
would represent a numeric data value for the item voltage within the asset. Whereas
"voltageUnit" : "volts"
Is string data for that same asset. Other data may be presented as arrays
"acceleration" : [ 0.4, 0.8, 1.0 ]
would represent acceleration with the three components of the vector, x, y, and z. This may also be represented as an object
"acceleration" : { "X" : 0.4, "Y" : 0.8, "Z" : 1.0 }
both are valid formats within FogLAMP.
An example payload with a single reading would be as shown below
[
{
"timestamp" : "2020-07-08 16:16:07.263657+00:00",
"asset" : "motor1",
"readings" : {
"voltage" : 239.4,
"current" : 1003,
"rpm" : 120147
}
}
]